

Cromatest
378 results
-
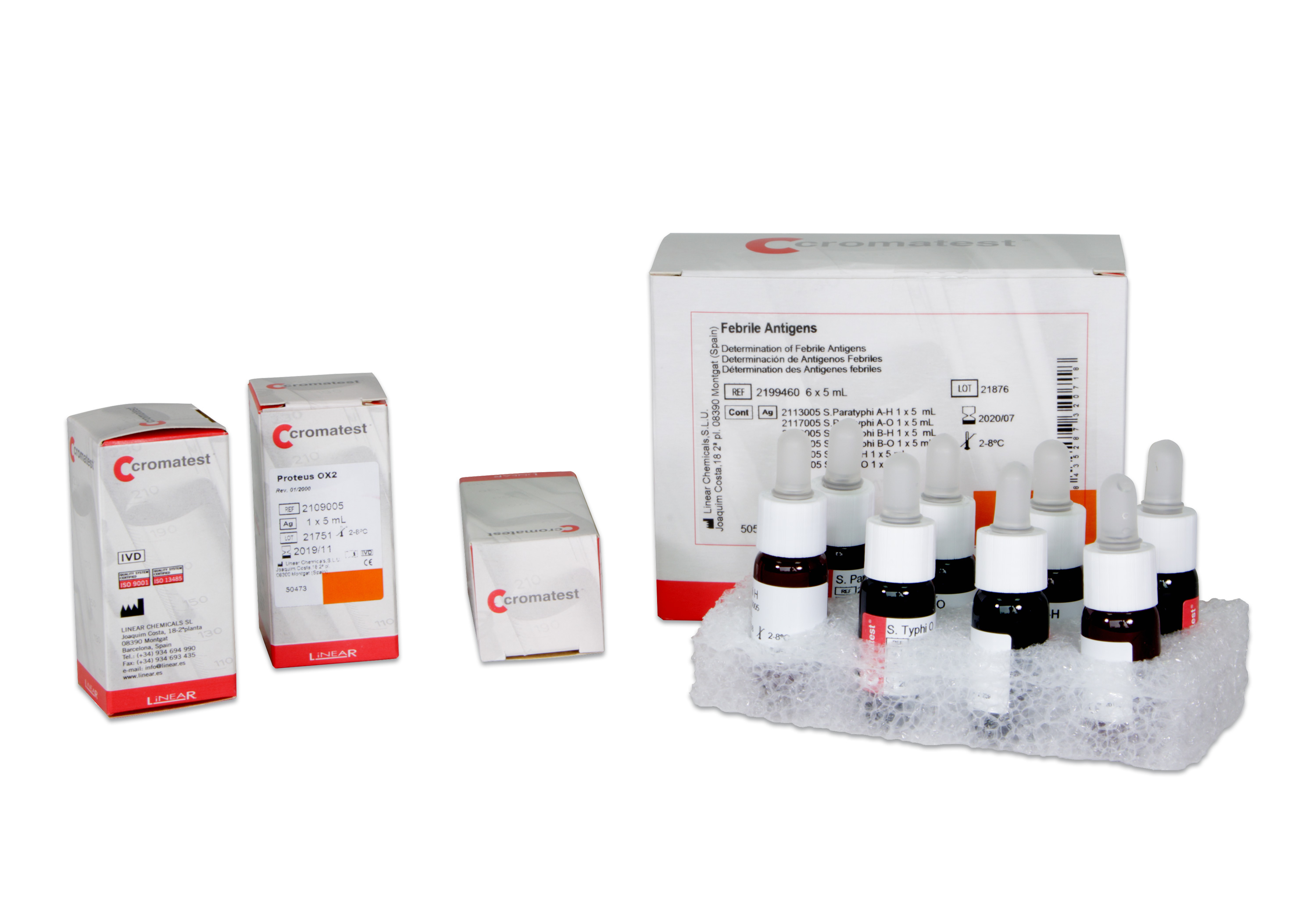
S. Paratyphi A-H 5ml
2113005CROMATEST colored antigens are standardized suspensions of dead bacteria prepared for the detection and semiquantification by agglutination in a slide or tube of human serum agglutinins, a group of antibodies that develop during some febrile infections such as brucellosis, salmonellosis, and certain rickettsioses.
-

S. Paratyphi A-O 5ml
2117005CROMATEST colored antigens are standardized suspensions of dead bacteria prepared for the detection and semiquantification by agglutination in a slide or tube of human serum agglutinins, a group of antibodies that develop during some febrile infections such as brucellosis, salmonellosis, and certain rickettsioses.
-
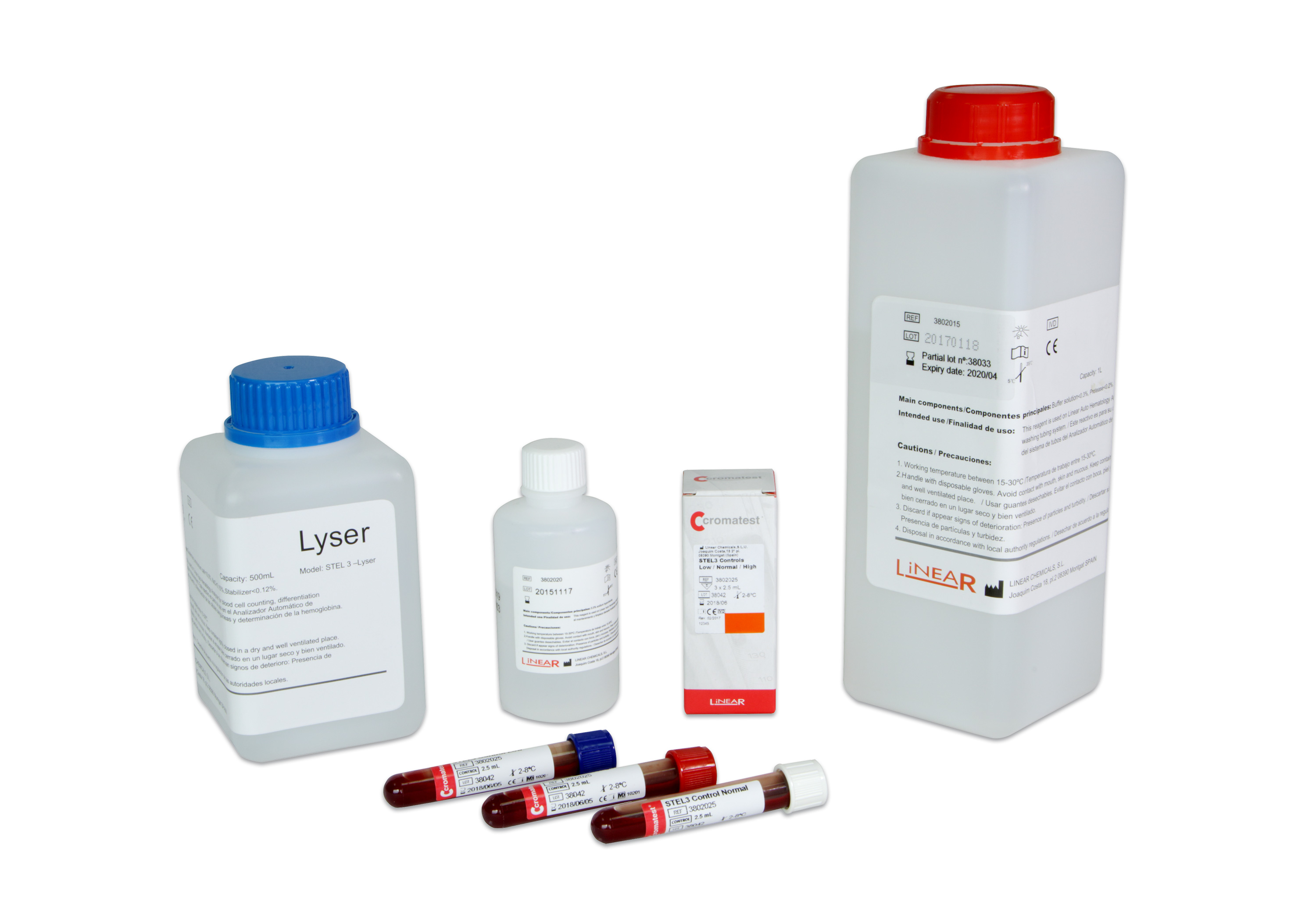

STEL3 – Extra Cleaner 20 L
3802020 -

STEL3 – Hematology Control
3802025 -

STEL3 – Diluent 1x1 L
3802005 -

STEL3 – Cleaner 3802015
3802015 -
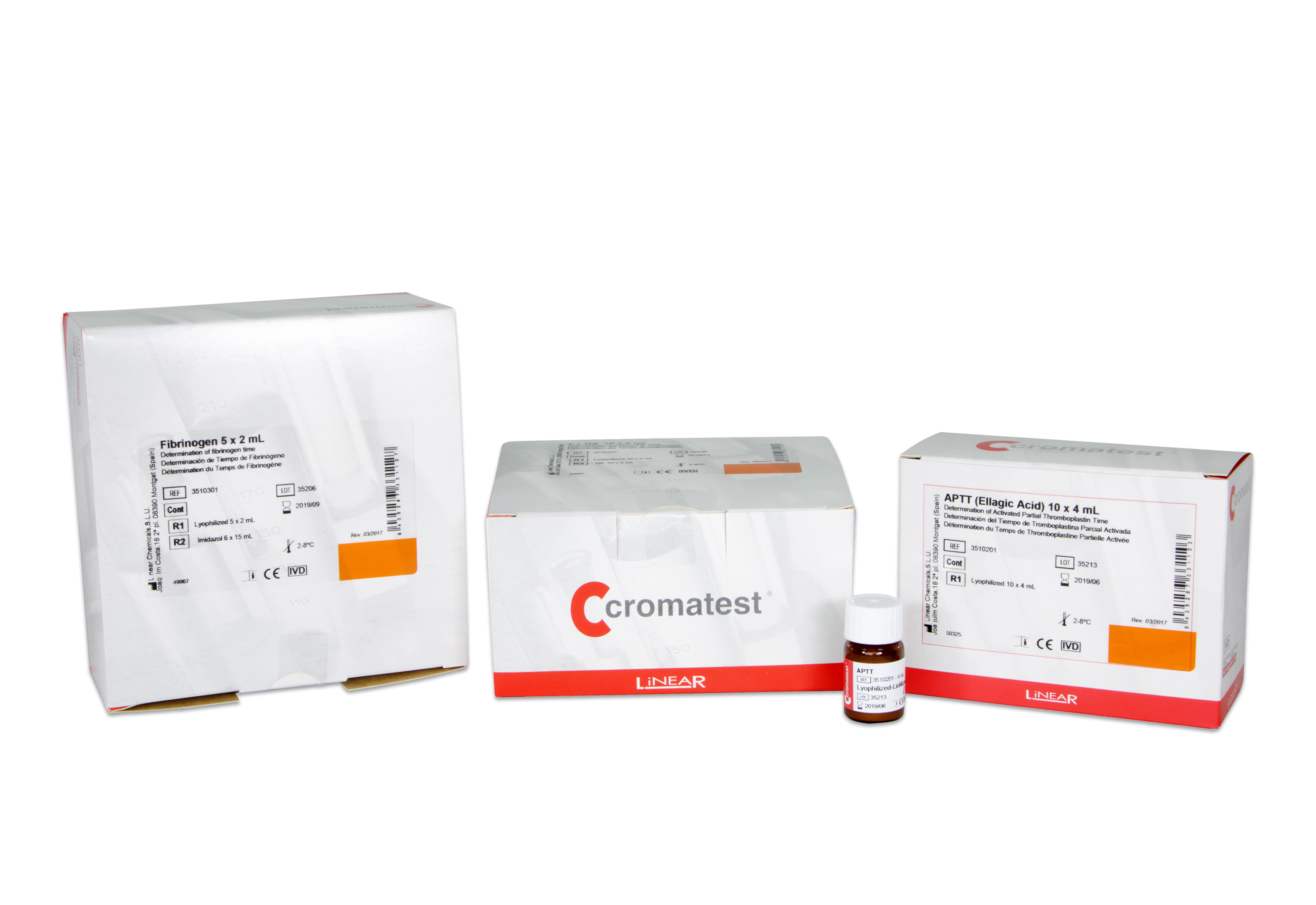
Plasma Control Level 2 10x1 ml
3520205 -

Plasma Control Level 2 5x1 ml
3520201 -

PT-HS 10x5 ml
3510105The blood's ability to form a fibrin clot through the extrinsic hemostatic pathway requires thromboplastin, calcium, and factors I, II, V, VII, and X. The Linear PT-HS reagent is a source of thromboplastin and calcium that specifically activates factor VII and the extrinsic pathway of coagulation. Factors of the intrinsic coagulation pathway (VIII, IX, and XII) are not involved, so deficiencies in these factors are not detected by the PT test.
-

Fibrinogen 1x36 ml
3510301The Clauss method measures the conversion rate of fibrinogen to fibrin in the presence of an excess of thrombin, and this method has proven to be a rapid, sensitive, and accurate test. When the diluted plasma coagulates due to excess thrombin, the fibrinogen level is inversely proportional to the coagulation time.
-

PT-HS 5x2 ml
3510101The blood's ability to form a fibrin clot through the extrinsic hemostatic pathway requires thromboplastin, calcium, and factors I, II, V, VII, and X. The Linear PT-HS reagent is a source of thromboplastin and calcium that specifically activates factor VII and the extrinsic pathway of coagulation. Factors of the intrinsic coagulation pathway (VIII, IX, and XII) are not involved, so deficiencies in these factors are not detected by the PT test.
-

Plasma Control Level 1 10x1 ml
3520105